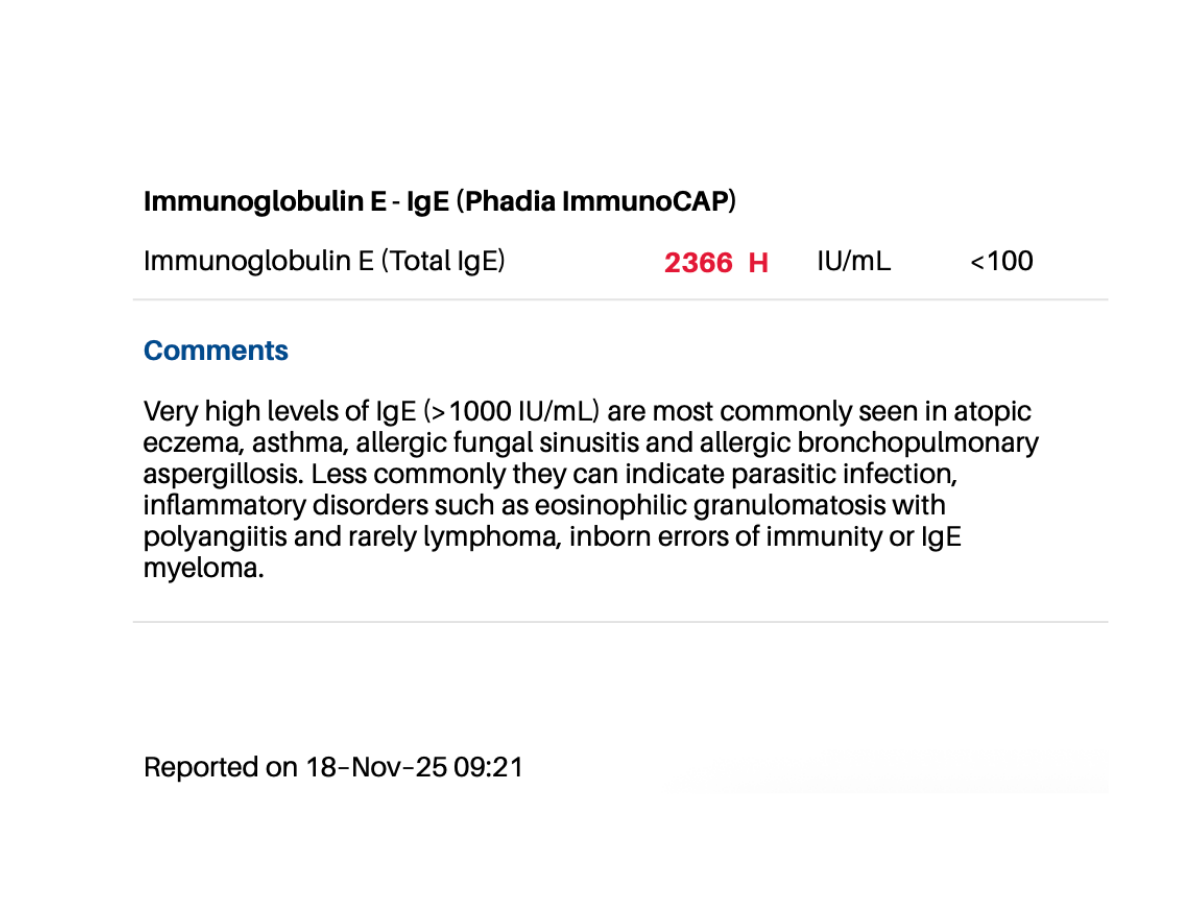
A Total IgE consistently exceeding 2300 IU/mL defines a system in a state of permanent biological extremity. Clinical outcomes are determined multi-factorily. The 2022 and 2025 test results below used different methodologies and although not directly comparable in magnitude document geographical variability as a significant unavoidable causal factor.
Both demonstrate significant grass pollen sensitisation, with the rural environment producing markedly higher clinical burden than the urban setting - this is not comparing apples to oranges, but rather comparing two different measures of the same biological reality that document geographical variability as a significant unavoidable causal factor.
March 2022 (Rural)
Immunoglobulin E (Total IgE)
November 2025 (Urban)
Immunoglobulin E (Total IgE)
March 2022 (Rural)
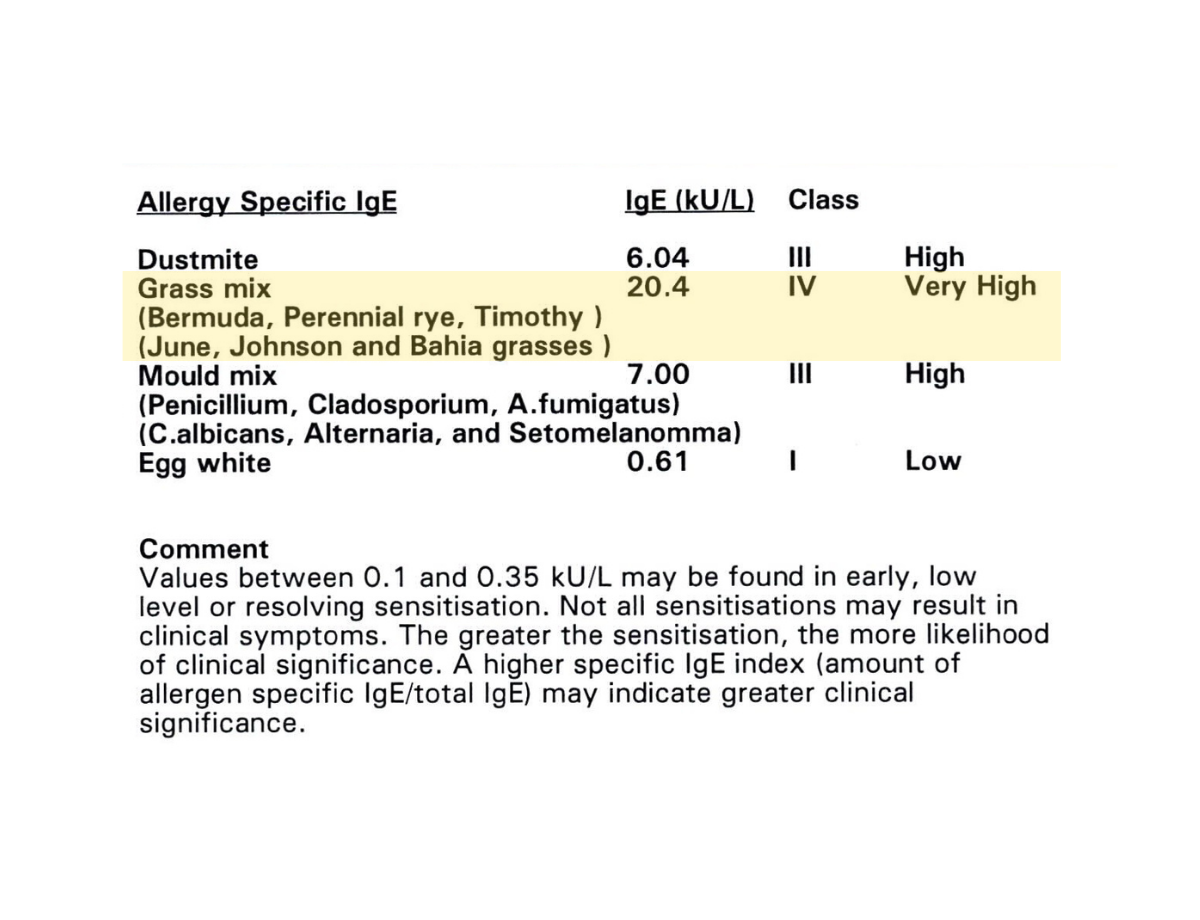
Timothy Grass Mix (VERY HIGH)
November 2025 (Urban)
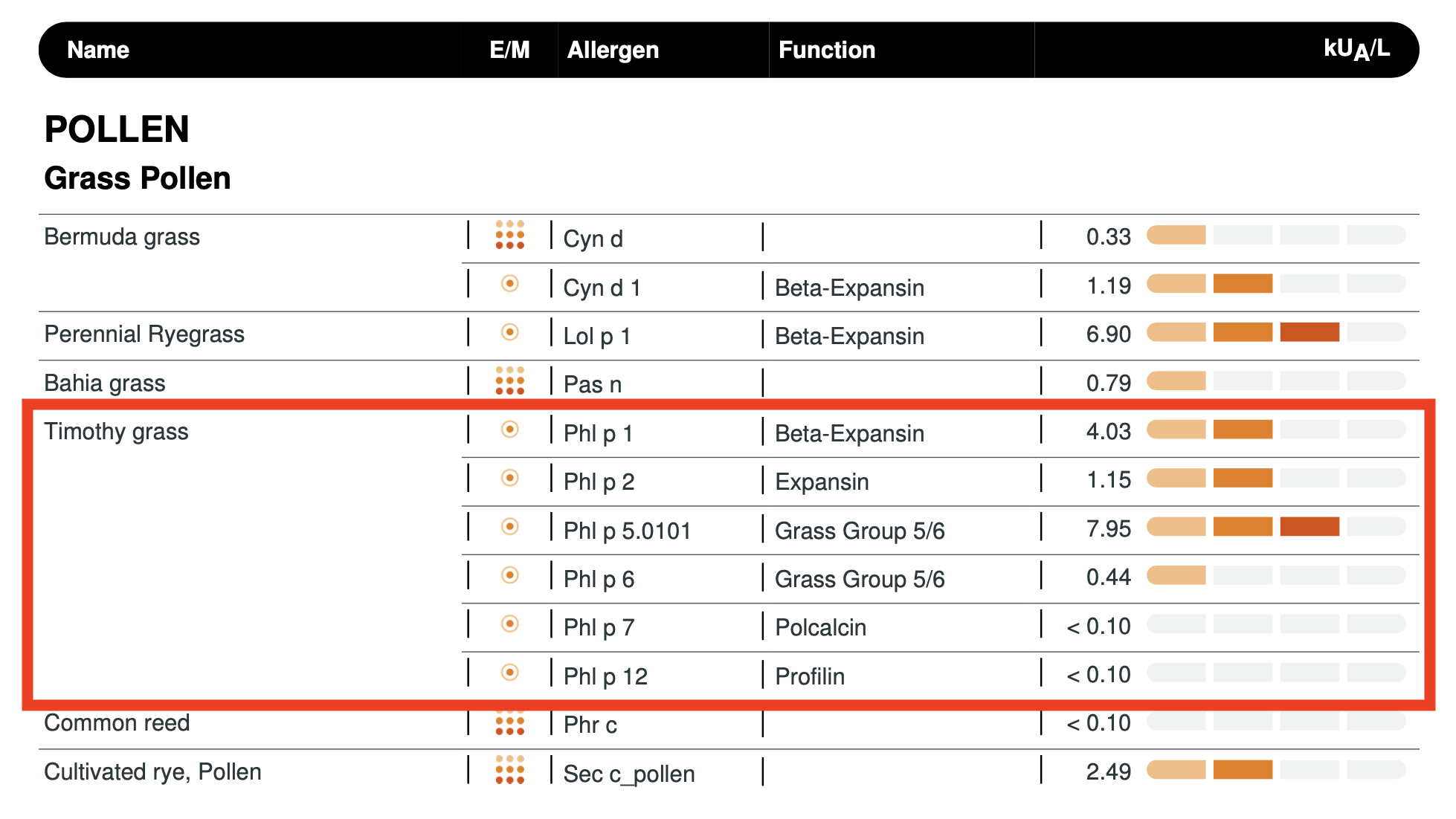
Timothy Grass (Phl p 5.0101) (HIGH)
Laboratory Result Extracts
2022 Total IgE

2022 Grass Spike
2025 Total IgE
2025 Grass Baseline
In late March 2020, as global lockdowns commenced, relocation to a small rural village without the ability to drive created a state of biological confinement. Timothy Grass Mix test results from March 2022 indicate that the rural environment imposed a constant pathogenic exposure that exceeded what an already over-sensitised system could tolerate following eight years of cumulative sensitisation events and five relocations.
This sustained environmental exposure correlated with a period of marked systemic decline and although it does not establish geography as a singular causal driver, it demonstrates a biologically plausible and temporally aligned exposure variable that materially altered cumulative allergen load.
Persistently elevated total IgE (2308 IU/mL), combined with ubiquitous grass pollen exposure, functioned as a continuous immunological load that lowered the system’s allostatic threshold, coinciding with the onset of (previously exceptional) balance deterioration, worsening respiratory dysfunction and broader systemic decline.Relocation to an urban environment in May 2022 was associated with a significant reduction in this specific allergen burden and a partial restoration of clinical baseline.
In October 2023, two further major sensitisation events occurred within days. Beer (yeast), prawns (tropomyosin) and consumption of 100% yeast-based Inner Health Plus Travel Capsules (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) - precipitating further balance deterioration, recurrent falls, a diagnosis of colitis and emergency hospital admission.
The cumulative effect led to approximately two years of near-total functional incapacitation, characterised by escalating systemic reactivity, minimal recovery and confinement to bed.
In October 2025, following self-directed review of historical treatment response and mast cell physiology, the author independently identified the need to reintroduce mast cell stabilisation using sodium cromoglycate, which he had been treated with from infancy. This was associated with an acute reduction of approximately 60% in symptoms and reactivity within weeks, including substantial vestibular improvement, massively reduced systemic inflammation and progression toward pre-2015 functional capacity.
The Timothy Grass findings confirm that geography functioned as an unrealised and/or misunderstood active biological factor. Beyond contributing to overall immunological load, the rural environment produced a sustained and biologically significant grass-allergen signal in a system already operating near its tolerance limit.
While the magnitude of exposure cannot be directly quantified across differing assay methods, the pattern indicates an environmental burden incompatible with stability. This principle plausibly extends to other environmental triggers including yeast, mould, dust mites and pollens. Different locations present different allergen profiles. In this context, relocation may function either as a clinical intervention or as a geographic liability.

